Title page

期刊:Accepted at NPJ Digital medicine
年份:2021
github链接:无
pdf链接:http://arxiv.org/abs/2108.02476
数据集链接:https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1e2t5HhQf08sTAE_CPRNVgpi6YUKgQSHn?usp=sharing
Summary
- GI-Genius团队,使用白光(WL)内窥镜视频流实时(50-60ms延迟)无缝进行息肉的CADx。
- 人机比对:使用在线平台,分为10名专家和11名非专家内窥镜师,二分类:”腺瘤性“与”非腺瘤性息肉“。
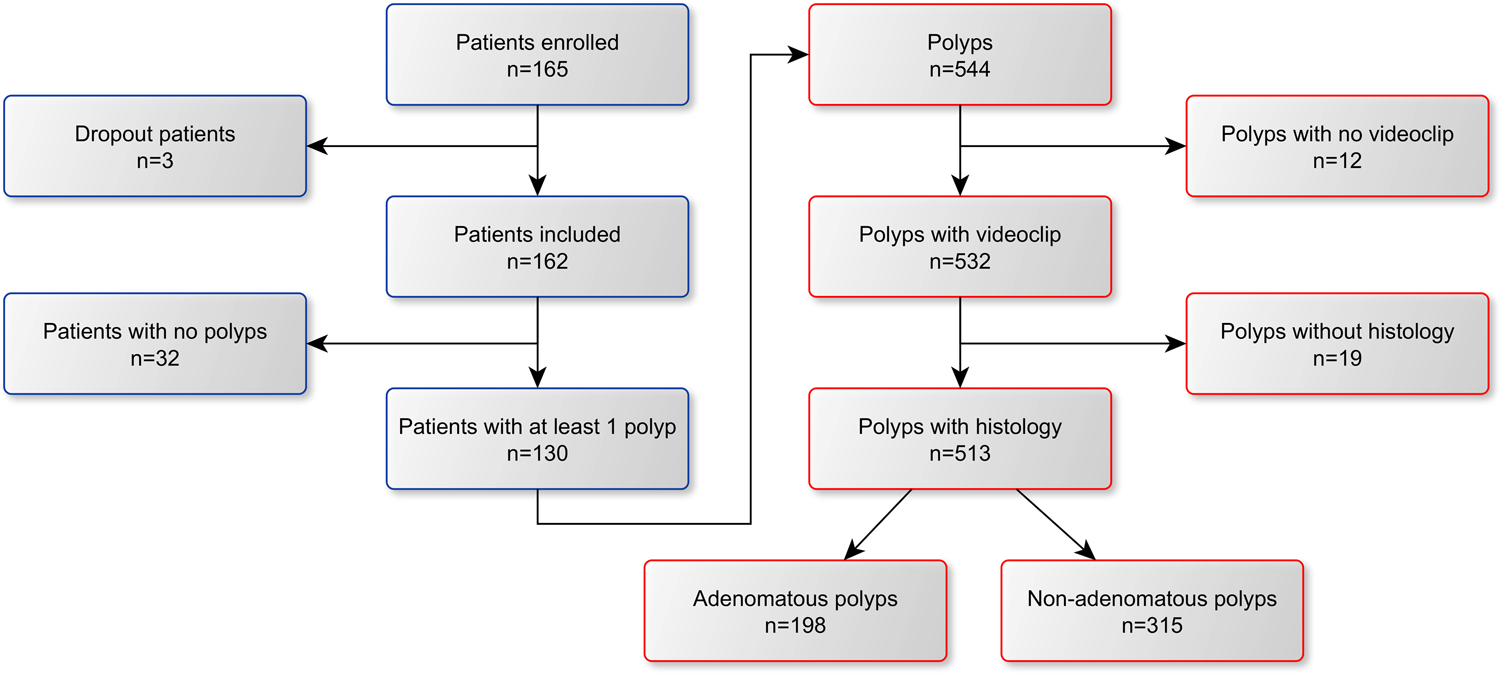
- 评估了165例患者的513颗息肉(198腺瘤,315非腺瘤)。以组织病理学为参考标准,发现WL中的CADx准确度与内窥镜检查专家的准确度相当。此外,WL中的CADx准确性优于非专家内窥镜师的准确性,BL中的CADx准确性与之相当(CADxBL/CADxWL;或0.886[0.612–1.282])。
Methods
- CADx模型的具体算法
- CADx系统包括两个模型,分别处理两个卷积神经网络模型的输出。
- 息肉特征网络(Polyp characterization network),它有两个目的:(1)将单个视频帧中检测到的每个息肉分类为“腺瘤”或“非腺瘤”息肉;(2)为当前帧中检测到的每个息肉提供息肉图像外观描述descripter,用于息肉跟踪。
- 生成bounding box \({\left\}}}_{k}\right\}}_{k = 1}^{K}\)
- bounding box + 50px边界,rescale到512×512,送入ResNet18用于分类,并得到介于[0,1]的score \({\left\}}}_{k}\right\}}_{k = 1}^{K}\) ,
- 分类损失函数:\(}}}_{cl} = BCE\)
- Polyp re-identification algorithm
- 为了对每一个捕获到的息肉获得一个时间加权决策
- 特征网络编码器的最后加了一个CNN分支 → An 8k-dimensional feature descriptor \({\left\}}}_{}\right\}}_{k = 1}^{K}\) for each input cropped image \(X_{t,i}\) ,然后从\(f_{t,i}\) 重建 \(\hat{X}_{t,i}\),第二个损失函数 \(}}}_{rec}=}}}_{MSE}({\hat}}}}_{t,i},}}}_{t,i})\)
- \[}}}_{tot}=}}}_{rec}+}}}_{cl}\]
- Hungarian (Kuhn–Munkres) algorithm 用于对 \(}}}_{t}\) 进行追踪
- 息肉成像质量网络,每个检测到的息肉提供成像质量分数,表示息肉特征在当前视频帧中成像的清晰度,减少噪声。该算法是一种时间聚合算法,该算法为每个跟踪的息肉聚合逐帧分类和成像质量信息,并基于移动的时间窗口提供实时决策。
- Four types of different predictions can be produced by the algorithm: “adenoma”, “non-adenoma”, “no-prediction” or “analysing”. “analysing” is printed near the polyp to communicate to the endoscopist to keep imaging the target polyp until the minimum number \(N_m\)(预先设定) of frames is reached.
- When the minimum number of frames \(N_m\) is reached, the number of non-adenoma and adenoma frame by frame predictions are computed with the introduction of two hyperparameters \(δ_{low}\) and \(δ_{high}\) that define when a frame by frame prediction has low confidence: \(N_{na} = {c_{k,j}} ∈ {L_j}∣(c_j < 0.5 − δ_{low}) ∧ q_{i,t} ≥ 1}\ and\ N_a = c_{k,j} ∈ {L_j}∣(c_j > 0.5 + δ_{high}) ∧ q_{i,t} ≥ 1}\). If Nna or N**a is the majority of the total number of valid frames the algorithm prints “adenoma” or “non-adenoma” on the bounding box, otherwise “no-prediction” is printed.
- 息肉特征网络(Polyp characterization network),它有两个目的:(1)将单个视频帧中检测到的每个息肉分类为“腺瘤”或“非腺瘤”息肉;(2)为当前帧中检测到的每个息肉提供息肉图像外观描述descripter,用于息肉跟踪。
- CADx系统包括两个模型,分别处理两个卷积神经网络模型的输出。
- 人机比对的protocals
Result-show
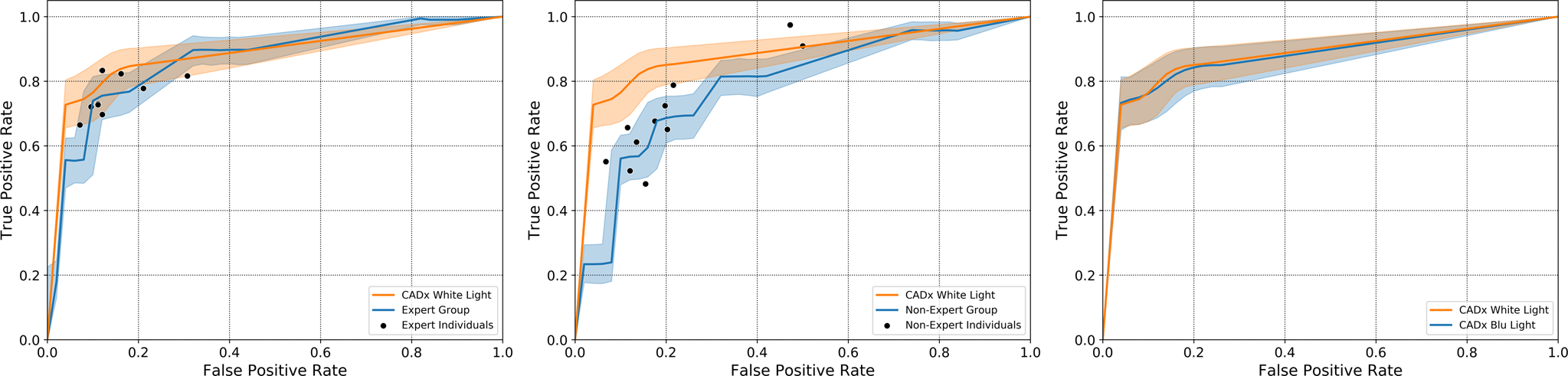
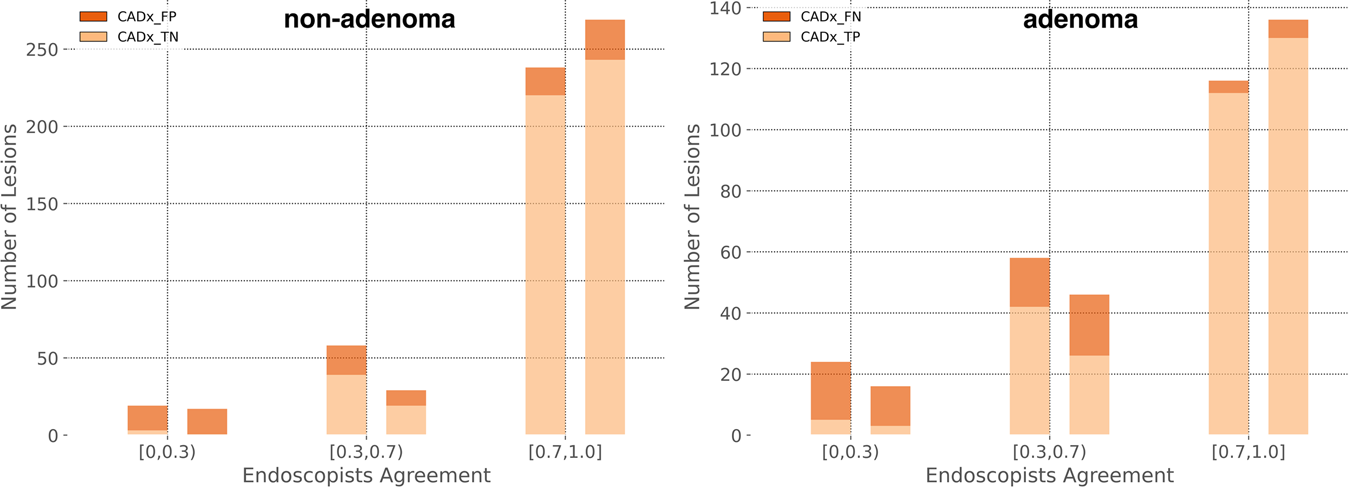
A noteworthy result of this study was the disagreement observed between a large panel of endoscopists with heterogeneous expertise and histology
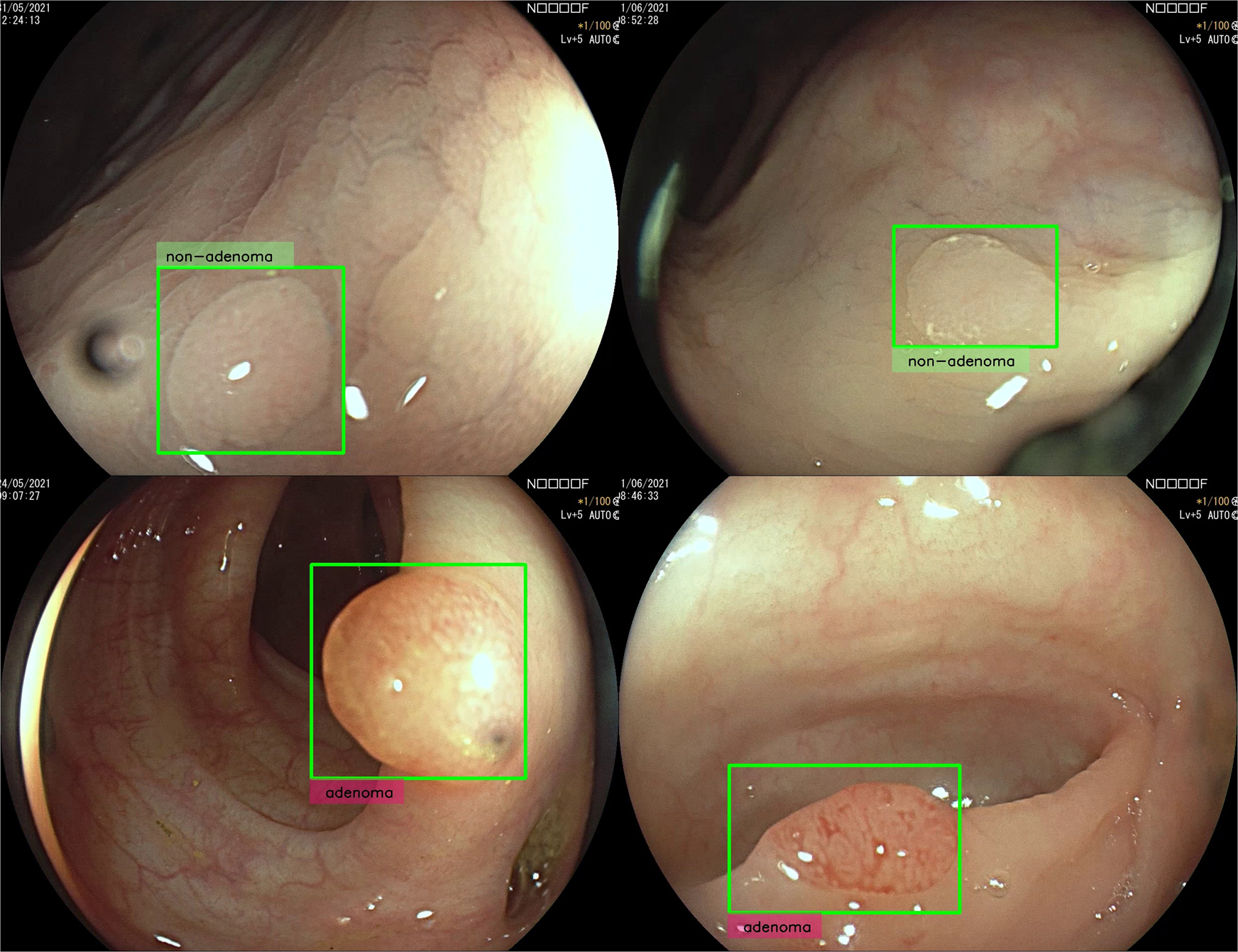
启发和思考
- Discussion
- we have developed for the first time an intelligent medical device that can perform the task of OC in real-time on unaltered conventional WL videos
- 文章提出了一个观点:the process of OC can be considered as a weighted average of different features over time(之前的研究都没有考虑这一点,导致分类结果不一致)
- 不足:单中心;二分类,并且将SSL分类到了非腺瘤性息肉(作者说数据集太少)
代码注释
1
# 无代码