Title page
会议:Accepted at MICCAI-21
年份:2021
github链接:(无内容)
pdf链接:http://arxiv.org/abs/2108.02476
数据集链接:https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1e2t5HhQf08sTAE_CPRNVgpi6YUKgQSHn?usp=sharing
Summary
- 使用白光直接分类的原因
- the widely used colonoscopy devices only have WL and NBI modes
- 切换肠镜的模式时,可能遗漏掉一些息肉
- 缺点:白光分类的准确度低与NBI、BLI等模式下的图像
- teacher-student结构,直接使用白光肠镜的图像来进行息肉的光学活检分类
- NBI数据用于训练teacher网络并通过特征转移指导student网络
- 特征转移通过domain alignment和对比学习实现
- Student网络最终能直接提取白光肠镜图像对齐后的特征
- 发布了第一个包含WL-NBI对的公共可用配对CPC数据集
Workflow
we adopt domain alignment to shift the distribution from WL features to NBI features during training, with the assistance of corresponding paired NBI images.
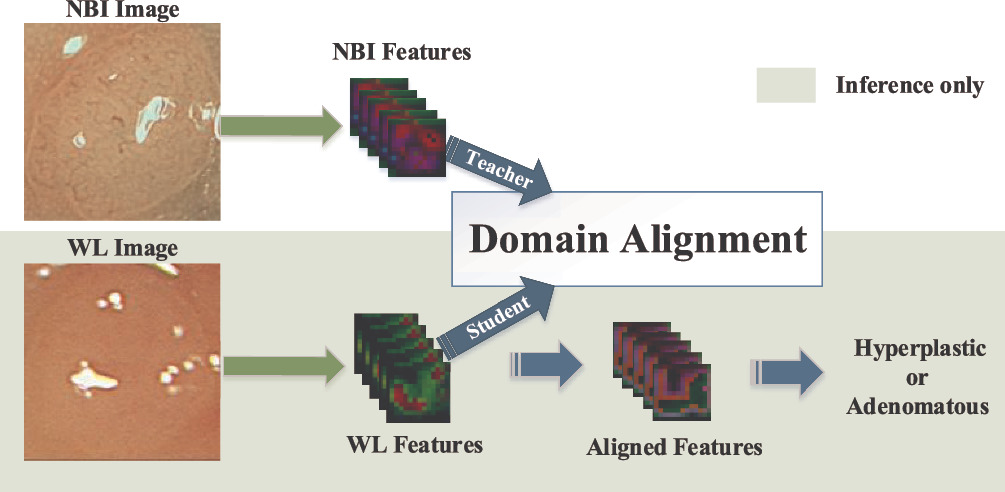
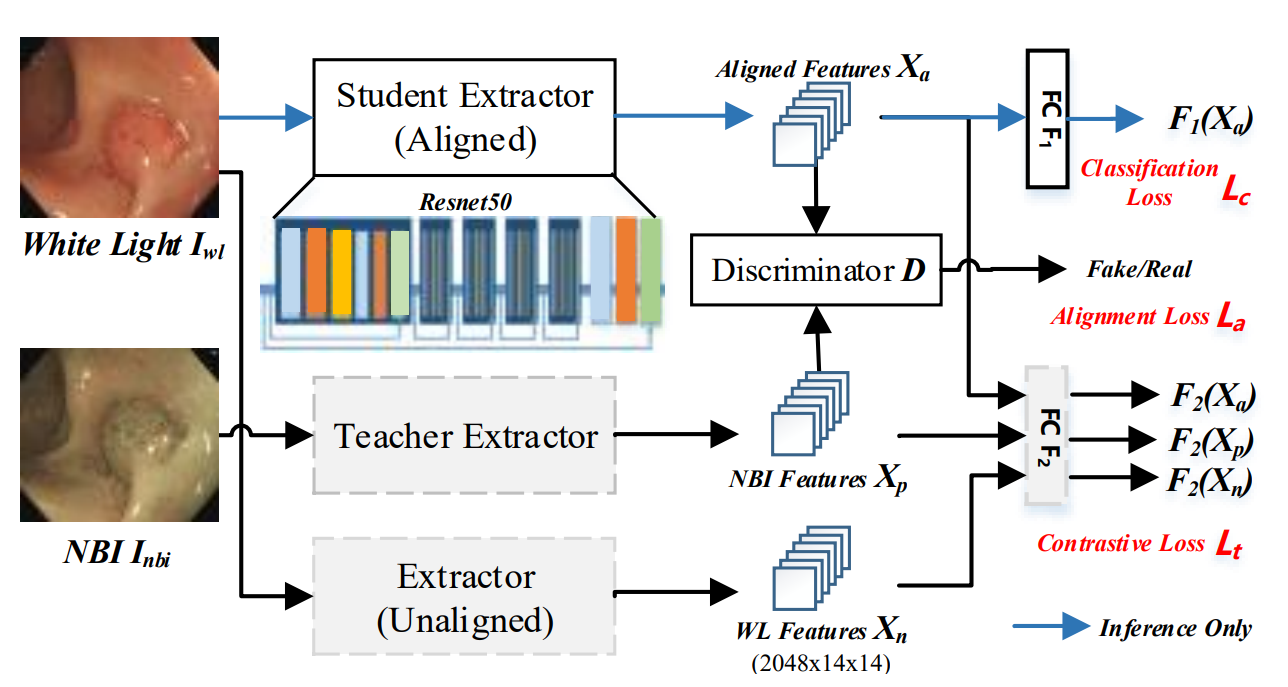
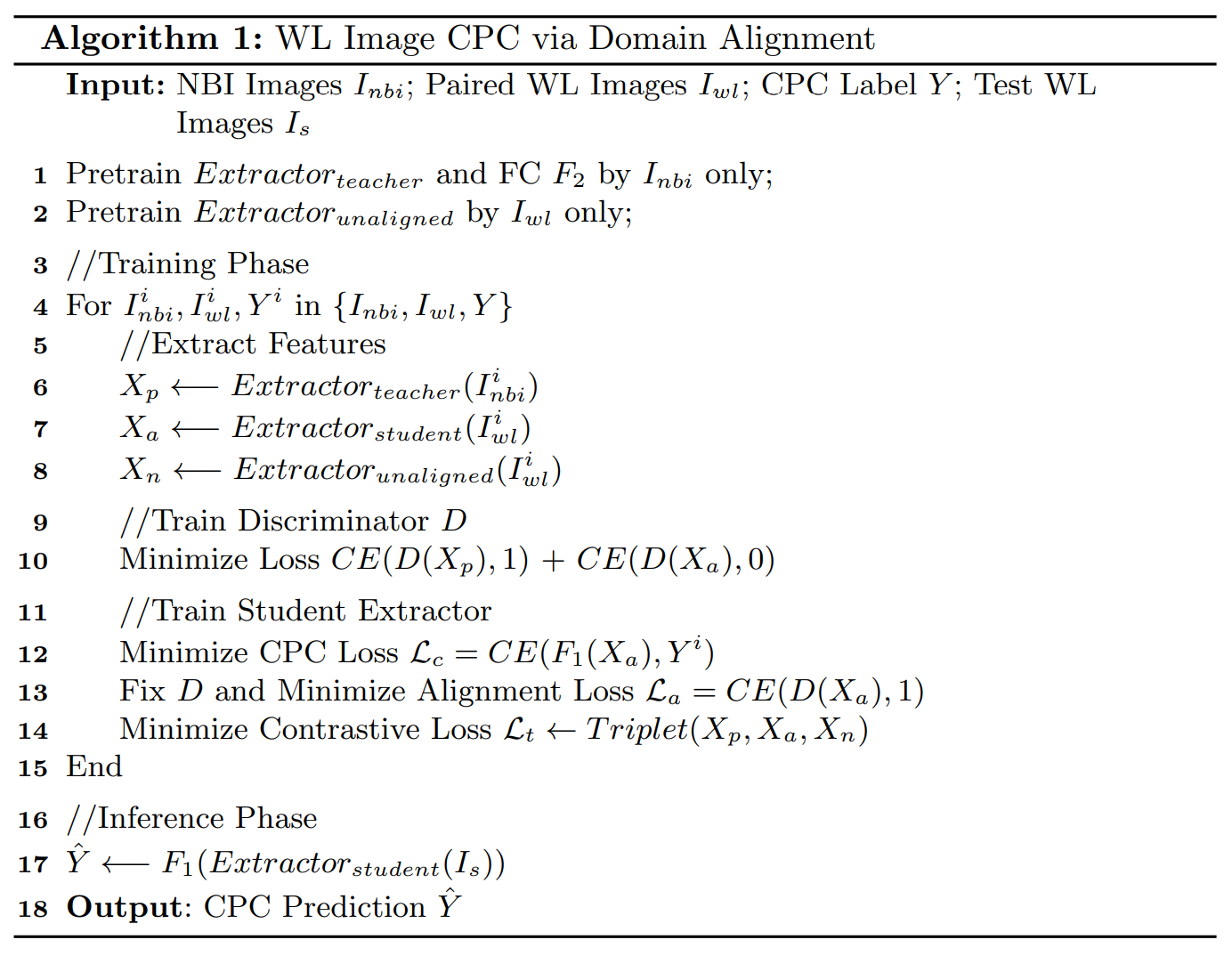
Methods
Domian alignment
- DA: align feature distributions between the source and target domains.
Adversarial Learning for Domain Alignment
- 分别使用NBI图像和WL图像,预训练teacher和unaligned extractors,固定参数
- A discriminator D is introduced to align the WL features Xa with the rich NBI features Xp.
- The discriminator is optimized to distinguish between aligned WL features Xa and NBI features Xp (i.e., NBI features are real and WL features are fake)
- Student Extractor:生成器;D:2层卷积层和两层全连接层
- Alignment loss La:用于对齐Xa和Xp
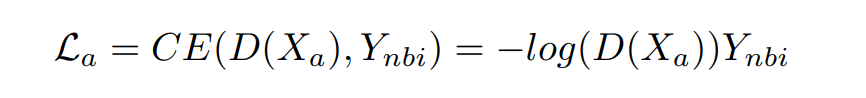
Contrastive Learning
额外引入了 Contrastive Loss Lt:使得Xa与Xp尽可能一致的同时,远离Xn
We take NBI features Xp as positive samples and unaligned WL features Xn as negative samples. To optimize aligned features Xa, the Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence is adopted to constrain the distribution distance from Xa to WL features Xn (i.e., negative samples) and NBI features Xp (i.e., positive samples) in high-level semantic space.

Dataset setting
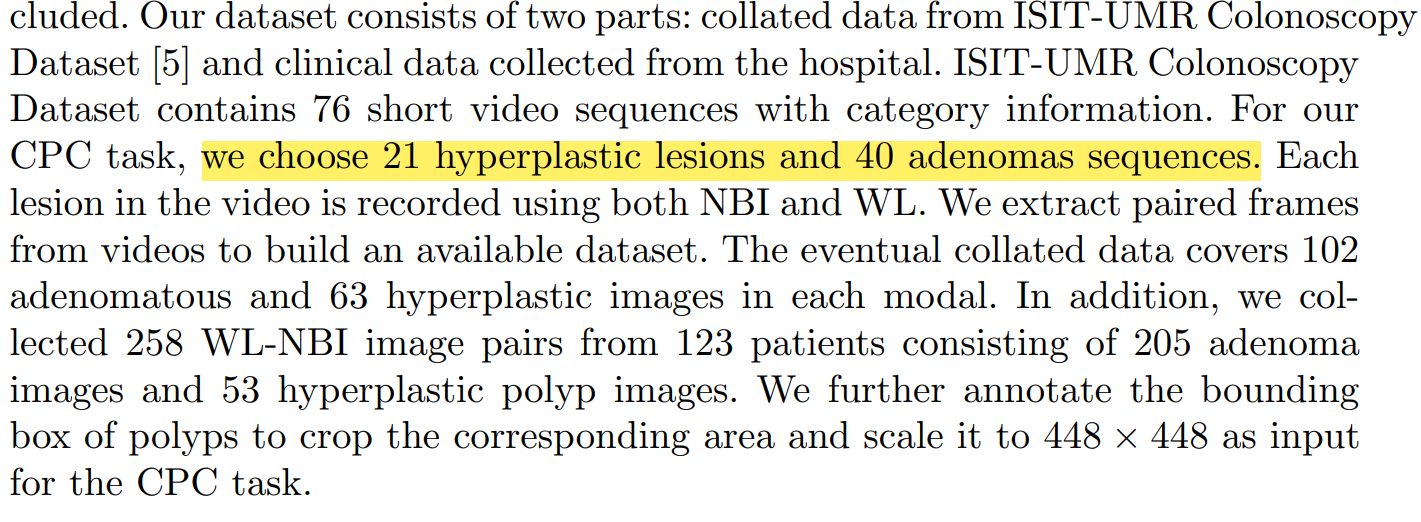
Result-show
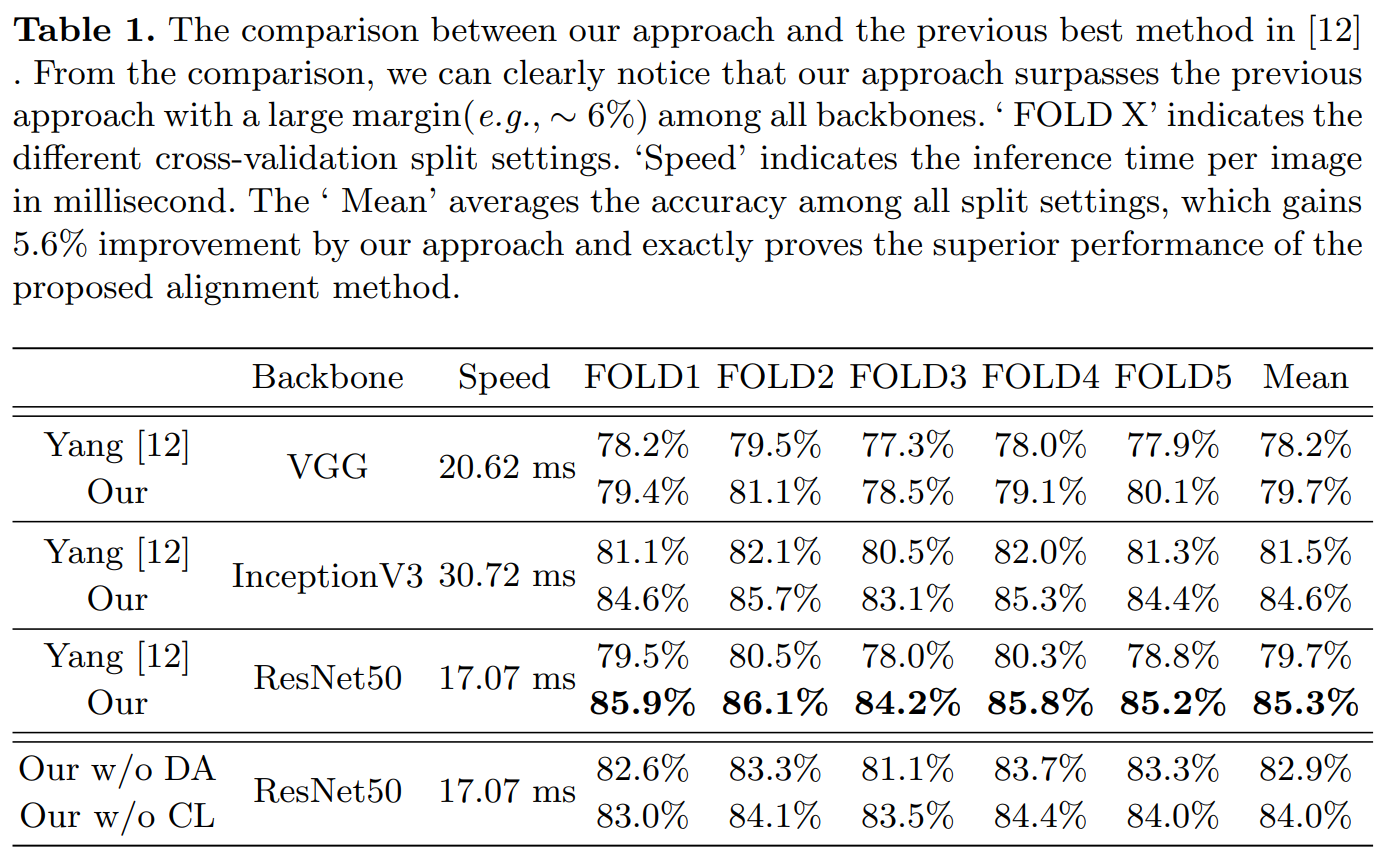
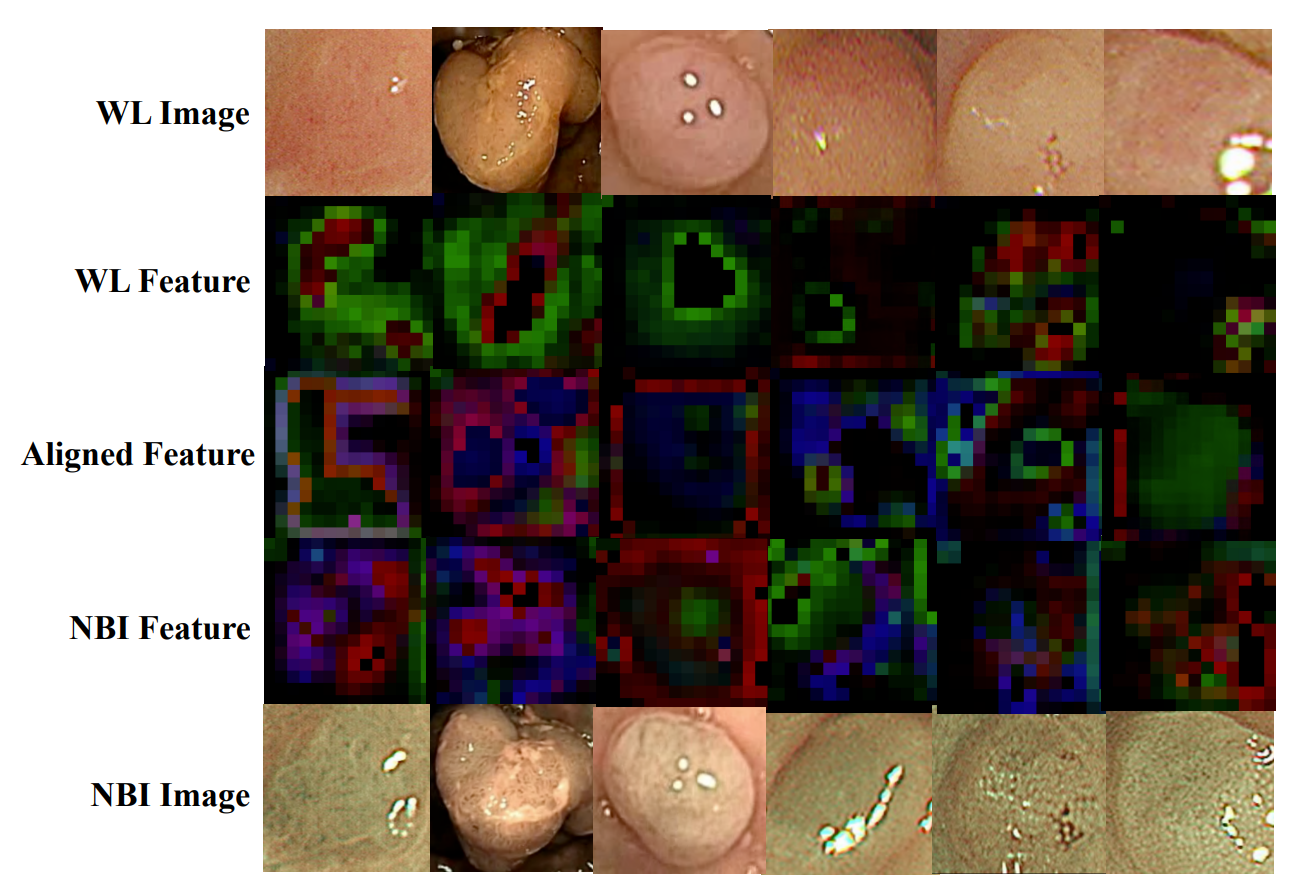
启发和思考
- 使用了domain alignment的方法,使得NBI的domain knowledge被用于基于WL的息肉分类中
- 不足:要获得完美的pairs难度过大,是否可能,仅基于NBI的图像,即可很好地进行领域知识的学习
- 对比学习的思想和GAN的思想引入,多任务学习(分类+对齐+对比loss)
代码注释
1
# 无代码